There must be ‘justice and accountability’ for infected blood ‘wrongdoings’ – PM
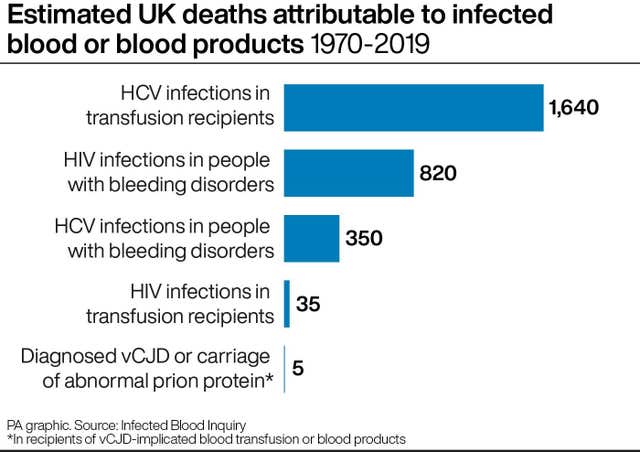
Some 30,000 people were affected by the worst treatment disaster in the history of the NHS.

There must be “justice and accountability” for any “wrongdoing” when it comes to the infected blood scandal, the Prime Minister has said.
Rishi Sunak said victims affected by the worst treatment disaster in the history of the NHS have “waited an incredibly long time for justice and the truth”.
The comments come as people affected by the scandal are waiting to hear details about how much they will be paid in compensation.
More than 30,000 people were infected with deadly viruses between the 1970s and early 1990s as they received blood transfusions or blood products while receiving NHS care.
Mr Sunak issued a “wholehearted and unequivocal” apology to the victims on Monday, saying the publication of the report into the disaster was “a day of shame for the British state”.
He promised to pay “comprehensive compensation” to those affected and infected by the scandal, with details expected to be revealed by Cabinet Office Minister John Glen in Parliament on Tuesday.
Speaking to reporters on a trip to Austria on Tuesday, Mr Sunak said “As I said yesterday in Parliament, it was a day of shame for the British state.
“That is why I, rightly as Prime Minister, offered an unequivocal apology to everyone affected by this appalling scandal.
“The infected, the affected, everyone impacted in the community, they have fought under considerable pressure facing prejudice over many decades.
“Anyone reading the report will have found it harrowing, indeed devastating, and I am glad that yesterday was a moment for reflection on everything that has happened, and their voices could be heard and they received the apology that they so rightly deserved.”
Asked if there should be criminal prosecutions of those found to have done wrong during the course of the scandal, Mr Sunak said: “As I said yesterday, anyone, people, individuals, where there is evidence of wrongdoing, of course there must be justice and accountability for that.
“But the report is very long, it is very comprehensive, and what I am committed to is the Government will now take the time to go through it properly and rigorously before responding in Parliament, and, of course, any individual cases will be a matter for the relevant authorities.”
Public inquiries are prohibited from making any recommendations about prosecutions but other countries affected by the scandal have seen ministers brought before the courts.
Max Hill, who left his role as director of public prosecutions for England and Wales in October, told Times Radio there is no time limit regarding how far back criminal prosecutions can go.
“The short answer is, if the evidence is there, there is no bar to an investigation and a prosecution,” he said.
“Now, sadly, corporate manslaughter came into force as a criminal offence on April 6, 2008 – much too late to deal with this case.
“However, there are other criminal offences which pre-date corporate manslaughter, where individuals have a duty of care and (if) they breached that duty in a gross way – that’s a legal term – they can be held liable.

Asked about the compensation scheme for victims, Mr Sunak said that an “enormous amount of work” has been going on over the past year to “make sure that we are in a position to now move as quickly as possible”.
Ministers have earmarked around £10 billion for a compensation package.
Members of the infected blood community have said they expect the Government is likely to set out how much compensation will be paid, simplified into a few categories, or tariffs.
This is likely to come under five main categories: injury, social impact, autonomy, care and financial loss.
The 2,527-page report from the inquiry, published on Monday, found the infected blood scandal “could largely have been avoided” and there was a “pervasive” cover-up to hide the truth.
Patients were knowingly exposed to unacceptable risks of infection.
Inquiry chairman Sir Brian Langstaff said “the scale of what happened is horrifying”, with more than 3,000 people dead as a result and survivors battling for decades to uncover the truth.
He said the “level of suffering is difficult to comprehend” and that the harms done to people have been compounded by the reaction of successive governments, the NHS and the medical profession.
Ministers failed to act in order to save face and expense, the inquiry said, with the current Government criticised for failing to act immediately on recommendations around compensation which were made last year.
Sir Brian said the contaminated blood disaster is “still happening” because patients who suffered “life-shattering” infections continue to die every week.





