NHS data shows continued drop in children receiving life-saving vaccines
Uptake of the first MMR dose at 24 months stood at 88.9% in 2023/24, the lowest since 2009/10.

The proportion of children receiving vaccines to protect against deadly diseases such as polio and measles continues to fall, new data shows.
NHS England figures covering 2023/24 show that not a single vaccine met the target needed to ensure diseases cannot spread among youngsters.
The World Health Organisation (WHO) says to achieve herd immunity (which stops illnesses transmitting across the population), at least 95% of children should receive their set of vaccine doses for each illness.
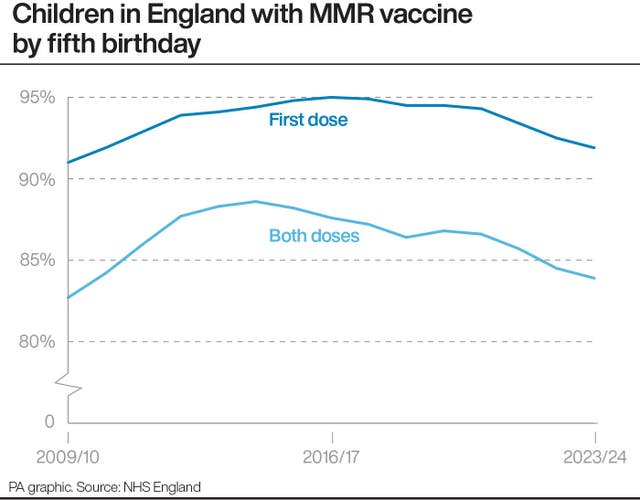
The new data shows 91.9% of five-year-olds had received one dose of the MMR (measles, mumps & rubella) vaccine, the lowest level since 2010/11, while just 83.9% had received both doses, the lowest since 2009/10.
Coverage of all the main vaccines fell year-on-year, with the largest drop seen for the Hib/MenC vaccine, which protects against Haemophilus influenzae type B and meningitis C.
This stood at 89.4% for children aged five in 2023/24, down from 90.4% in 2022/23 and the lowest level since 2011/12.
All other vaccines decreased by about 0.5%.
The last time any vaccine surpassed the target of 95% uptake was in 2020/21, when 5-1 vaccine coverage among five-year-olds stood at 95.2%.
The NHS says vaccines prevent more than 5,000 deaths and 100,000 hospital admissions each year in England.
Dr Vanessa Saliba, UKHSA consultant epidemiologist, said: “As a mum and doctor, I know the additional stress that comes with having a sick child.
“I encourage all parents to take up the offer of vaccinations for their children at the right time, to give them the best protection from preventable diseases.
“Childhood vaccines prevent babies and children from suffering needlessly and can even be life-saving.”
Dr Saliba said she was pleased that parents whose children have missed vaccines are coming forward in the light of campaigns, but she added: “We are a long way from ensuring all are protected and safe.”
UKHSA data shows that over 13% of previously unvaccinated children had one dose of the MMR jab between August 2023 and April 2024.
“It only takes one case of measles to get into a school or nursery where many children are unprotected for numbers to suddenly surge.
“It’s never too late to catch up.
“If you’re not sure if your child is up to date with all their vaccines, check their Red Book or contact your GP practice, who can book an appointment if needed. Don’t put it off, please act today.”
The new data shows 91.2% of children in England had completed the first course of the 6-in-1 vaccine by the age of 12 months in 2023/24, down from 91.8% the previous year.
The 6-in-1 vaccine protects against diphtheria, pertussis, tetanus, polio, disease caused by Haemophilus influenzae type B, and hepatitis B.
There has been a “general downward trend” in uptake of this vaccine since a peak of 94.7% in 2012/13, NHS England said.
It added that the NHS and GP practices have been sending reminders to the parents and carers of children not fully vaccinated.
Steve Russell, NHS national director for vaccinations and screening, said: “Too many children are still not fully vaccinated against diseases like measles and whooping cough, which can cause serious illness and are preventable.
“Vaccinations have been protecting children for decades and are offered free as part of the NHS routine immunisation programme, saving thousands of lives and preventing tens of thousands of hospital admissions every year.
“We would advise parents to urgently check their child’s vaccination records and ensure they’re protected from becoming seriously unwell.”
The data shows London had the lowest uptake levels in England of MMR, with 73.1% of children having received both doses by the age of five, and 86.2% of children getting all three doses of the 6-in-1 vaccine by their first birthday.





